Tradename:
Lasix
Composition:
Each tablet contains:
Furosemide 40 mg
Auxiliary components:
Lactose monohydrate, starch, talc, magnesium stearate.
Properties:
“Loop” diuretic; causes a fast, strong and short-term diuresis. Blocks the reabsorption of sodium and chlorine ions both in the proximal and in the distal parts of the renal tubules and in the thick segment of the ascending part of the Gentle loop. Furosemide has a pronounced diuretic, natriuretic and chloruretic effect. Due to the increase in the release of sodium ions, there is a secondary (mediated by osmotically bound water) enhanced excretion of water and an increase in the secretion of potassium ions in the distal part of the renal tubule. At the same time, the excretion of calcium and magnesium ions increases. Has secondary effects due to the release of intrarenal mediators and the redistribution of intrarenal blood flow. Against the background of the course of treatment, there is no weakening of the effect.
After oral administration of 40 mg of furosemide, the diuretic effect begins within 60 minutes and lasts about 3-6 hours (with reduced renal function – up to 8 hours). During the period of action, the excretion of sodium ions increases significantly, however, after its termination, the rate of excretion decreases below the initial level (“rebound” or
“cancellation” syndrome). The phenomenon is caused by a sharp activation of the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system and other anti-natriuretic neurohumoral regulation links in response to massive diuresis; stimulates the arginine-vasopressive and sympathetic systems. Reduces the level of atrial natriuretic factor in blood plasma, causes vasoconstriction. Due to the “rebound” syndrome, when taken 1 time / day, it may not cause a significant effect on the daily release of sodium ions and blood pressure.
Indications:
Edematous syndrome:
- with chronic heart failure;
- with chronic renal failure;
- with nephrotic syndrome (with nephrotic syndrome, the treatment of the underlying disease is in the foreground);
- with liver diseases;
-arterial hypertension.
Method of administration and dosage:
The tablets should be taken on an empty stomach without chewing and drinking plenty of fluids. When prescribing Furosemide, it is recommended to use its lowest dose, sufficient to achieve the desired effect. The maximum daily intake for adults is 1500 mg. The initial single dose in children is determined at the rate of 1-2 mg / kg of body weight / day with a possible increase in the dose to a maximum of 6 mg / kg / day, provided that the drug is taken no more often than after 6 hours.The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor individually, depending on from the testimony.
Dosing regimen in adults:
Edematous syndrome in chronic heart failure.
The initial dose is 20-80 mg / day. The required dose is selected depending on the diuretic response. It is recommended to divide the daily dose into 2-3 doses.
Swelling in nephrotic syndrome:
The initial dose is 40-80 mg / day. The required dose is selected depending on the diuretic response. The daily dose can be taken in one dose or divided into several doses.
Arterial hypertension:
Lasix can be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs. The usual maintenance dose is 20-40 mg / day. When adding furosemide to already prescribed drugs, their dose should be reduced by 2 times. In case of arterial hypertension in combination with chronic renal failure, the use of higher doses of the drug may be required.
Contraindications:
-Acute renal failure with anuria;
-severe hepatic failure, “hepatic” coma and precoma;
-Acute glomerulonephritis, pronounced disorders of the outflow of urine of any etiology (including unilateral urinary tract damage), hyperuricemia;
-decompensated mitral or aortic stenosis, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, increased central venous pressure (over 10 mm Hg);
- violation of water and electrolyte metabolism (hypovolemia, severe hyponatremia and hypokalemia, hypochloremia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia);
- digitalis intoxication;
-pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- age up to 3 years (solid dosage form);
- lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome (due to the presence of lactose monohydrate in the preparation);
- wheat allergy (not celiac disease);
-increased sensitivity to the active substance and to any of the components of the drug.
Patients who are allergic to sulfonamides (sulfonamide antimicrobials or sulfonylureas) may be cross-allergic to furosemide.
Precautions:
Before starting therapy with Lasix, the presence of pronounced violations of the outflow of urine should be excluded, patients with a partial violation of the outflow of urine need careful monitoring. Against the background of the course of treatment, it is necessary to periodically monitor blood pressure, the content of blood plasma electrolytes (including sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium ions), acid-base state,
residual nitrogen, creatinine, uric acid, liver function and, if necessary, appropriate correction of treatment.
Side effects:
From the side of the cardiovascular system: a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, collapse, tachycardia, arrhythmias, a tendency to thrombosis, a decrease in circulating blood volume.
From the side of the central nervous system: dizziness, headache, muscle weakness, cramps of the calf muscles (tetany), paresthesia, apathy, weakness, weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, confusion.
From the senses: impaired vision and hearing, tinnitus.
From the digestive system: anorexia, dryness of the oral mucosa, thirst, nausea, vomiting.
From the genitourinary system: oliguria, acute urinary retention (in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia), interstitial nephritis, hematuria, decreased potency.
From the side of water and electrolyte metabolism: hypovolemia, dehydration (risk of thrombosis and thromboembolism), hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, metabolic alkalosis.
Laboratory indicators: hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperuricemia, glucosuria, hypercalciuria, increased activity of hepatic transaminases, eosinophilia.
Storage method:
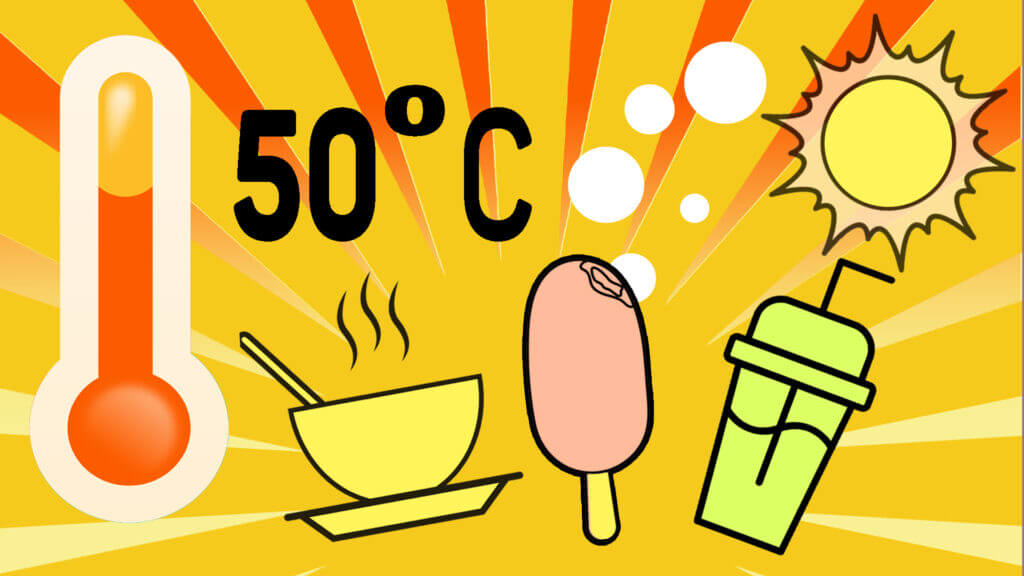
At a temperature not higher than 30 degrees.
Packaging:
The cardboard box holds 10 or 24 tablets.
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي