Tradename:
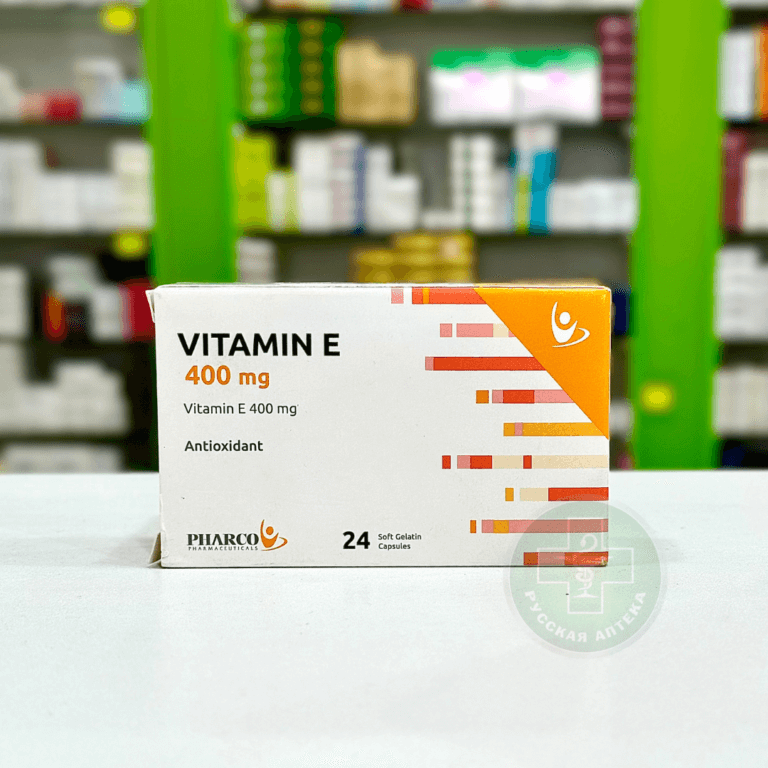
Vitamin E
Vitamin E
Structure :
Each softgel contains:
Vitamin E 400 mg
Pharmacological actions:
Vitamin E is considered one of the most important vitamins. Many of its actions are related to its antioxidant properties
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that prevents the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. It reacts with free radicals that cause oxidative damage to cell membranes without generating another free radical in the process.
Vitamin E protects red blood cells from hemolysis. Protection against damage by oxygen radicals is important for the development and maintenance of nerve and muscle function.
Pharmacokinetics:
The absorption of vitamin E from the gastrointestinal tract depends on the presence of bile and on the normal function of the pancreas. The amount of absorbed vitamin E varies widely from 20% to 80%. It enters the bloodstream through the chylomicrons in the lymph and binds to beta cells with lipoproteins. It is widely distributed in all tissues and is stored in adipose tissue. A certain amount of vitamin E is metabolized in the liver, tocopheronic acid glucuronides and its y-lactone are formed. Some of them are excreted in the urine, but most of the dose is slowly excreted in the bile. Vitamin E appears in the mammary gland and milk, however, it is poorly transferred across the placenta.
Indications for use:
Diseases associated with pathology caused by free radicals, for example:
– Cystic fibrosis and arthritic tissue damage.
– Chronic cholestasis.
– Some hemolytic anemias.
– Coronary artery disease.
– Atherosclerosis.
Dosage:
One capsule, one or more times a day, depending on the condition or as directed by a healthcare practitioner.
Contraindications:
Hypoprothrombinemia due to vitamin K deficiency
(may be aggravated by doses of vitamin E over 400 units per day)
Hypersensitivity to vitamin E
Side effects :
Vitamin E is generally well tolerated. Large doses can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain, and other gastrointestinal problems.
They have also been reported to cause blurred vision, dizziness, fatigue, and weakness.
Drug Interactions:
Various medications can interfere with the absorption of vitamin E, including cholestyramine, colestipol, and orlistat. High doses of vitamin E can increase the effect of oral anticoagulants.
Pregnancy and Lactation:
Placental transfer is incomplete, newborns receive 20 to 30% with breast milk.
Precautions:
High doses of vitamin E have been reported to increase bleeding in vitamin K-deficient patients, such as those taking oral anticoagulants. However, it has also been suggested that it may increase the risk of thrombosis in some patients.
Packing:
The box contains 24 capsules in 2 blisters, paper instructions.
Storage:
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 ° C in a dry place, away from light.
Keep out of the reach of children.
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي