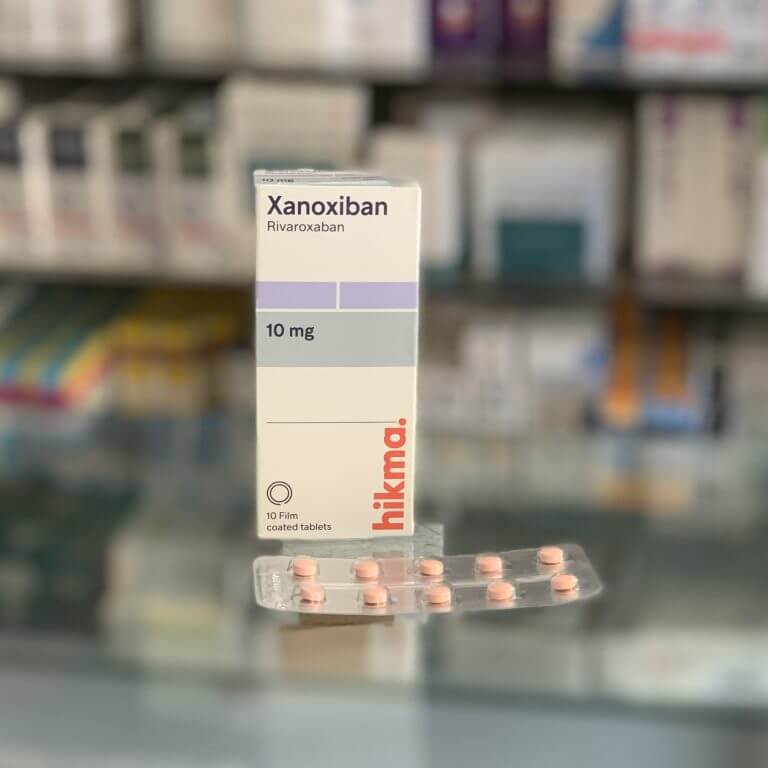
Tradename:
Xanoxiban
Xanoxyban
Compound:
Each tablet contains:
Rivaroxaban 15 mg
Auxiliary components:
microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose 5 cP (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 2910), lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate.
Properties:
Rivaroxaban is a highly selective direct factor Xa inhibitor with high oral bioavailability.
Activation of factor X to form factor Xa via the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways plays a central role in the coagulation cascade. Factor Xa is a component of the emerging prothrombinase complex, the action of which leads to the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. As a result, these reactions lead to the formation of a fibrin thrombus and activation of platelets by thrombin. One factor Xa molecule catalyzes the formation of more than 1000 thrombin molecules, which is called the “thrombin explosion”. The reaction rate of factor Xa bound in prothrombinase increases by 300,000 times compared to that of free factor Xa, which provides a sharp jump in the level of thrombin. Selective factor Xa inhibitors can stop the “thrombin burst”. Thus, rivaroxaban affects the results of some specific or general laboratory tests used to evaluate clotting systems.
Indications:
– prevention of stroke and systemic thromboembolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation;
-treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism and prevention of recurrence of DVT and PE.
Dosage and administration:
Use the drug during meals.
Prevention of stroke and systemic thromboembolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
The recommended dose is 20 mg 1 time / day.
For patients with impaired renal function (CC 30-49 ml / min), the recommended dose is 15 mg 1 time / day.
The recommended maximum daily dose is 20 mg.
Treatment of DVT and PE and prevention of recurrence of DVT and PE
The recommended initial dose in the treatment of acute DVT or PE is 15 mg 2 times / day for the first 3 weeks, followed by a transition to a dose of 20 mg 1 time / day for further treatment and prevention of recurrence of DVT and PE.
After at least 6 months of treatment for DVT or PE, the recommended dose of Xanoxiban® is 10 mg once a day or 20 mg once a day, depending on the individual risk of recurrent DVT or PE and the risk of bleeding.
Contraindications:
– hypersensitivity to rivaroxaban or any excipients contained in the tablet;
– clinically significant active bleeding (for example, intracranial bleeding, gastrointestinal bleeding);
– an injury or condition associated with an increased risk of major bleeding (for example, an existing or recent gastrointestinal ulcer, the presence of malignant neoplasms with a high risk of bleeding, recent trauma to the brain or spinal cord, recent surgery on the brain, spinal cord or eyes, recent intracranial hemorrhage, diagnosed or suspected esophageal varicose veins, arteriovenous malformations, vascular aneurysms or large anomalies in the structure of the vessels of the brain or spinal cord);
– concomitant therapy with any other anticoagulants, for example, unfractionated heparin (UFH), low molecular weight heparins (including enoxaparin, dalteparin), heparin derivatives (including fondaparinux), oral anticoagulants (including warfarin , apixaban, dabigatran), unless the patient is transferred from or to therapy with Xanoxiban®, or when UFH is given at low doses to maintain patency of a central venous or arterial catheter;
– liver diseases with coagulopathy, which causes a clinically significant risk of bleeding, including patients with cirrhosis of the liver of classes B and C according to the Child-Pugh classification;
– severe degree of renal dysfunction with CC <15 ml / min (clinical data on the use of rivaroxaban in patients of this category are not available);
-pregnancy;
– period of breastfeeding;
-children and adolescents under 18 years of age (efficacy and safety for patients of this age group have not been established);
– hereditary intolerance to lactose or galactose (for example, congenital lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption), since lactose is part of the medicinal product.
Precautionary measures:
The use of rivaroxaban is not recommended in patients receiving concomitant systemic treatment with azole antifungals (eg, ketoconazole) or HIV protease inhibitors (eg, ritonavir). These drugs are strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein. Thus, these drugs can increase the plasma concentration of rivaroxaban to clinical
and significant values (2.6 times on average), which can lead to an increased risk of bleeding.
However, the azole antifungal fluconazole, a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4, has a less pronounced effect on rivaroxaban exposure and can be co-administered with rivaroxaban.
Impaired kidney function
Rivaroxaban should be used with caution in patients with moderate renal impairment (CC 30-49 ml/min) who are receiving concomitant medications that may increase plasma concentrations of rivaroxaban.
Side effects:
anemia (including relevant laboratory parameters) – ocular hemorrhage (including conjunctival hemorrhage) – gastrointestinal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, bleeding gums, gastrointestinal bleeding (including rectal bleeding) – fever , peripheral edema, deterioration in general well-being (including weakness and asthenia) – hemorrhages after procedures (including postoperative anemia and bleeding from a wound), bruising – increased levels of transaminase – pain in the extremities. – dizziness, headache – bleeding from the urogenital tract (including hematuria, imenorrhagia), renal failure (including increased creatinine, increased urea levels) – epistaxis, hemoptysis – itching (including infrequent cases of generalized itching), rash, ecchymosis, skin and subcutaneous hemorrhages – arterial hypotension, hematoma .
Storage method:
At a temperature not higher than 30 degrees. In a dry place.
Package:
The carton contains 1, 2 or 3 blisters of 10 tablets.
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي