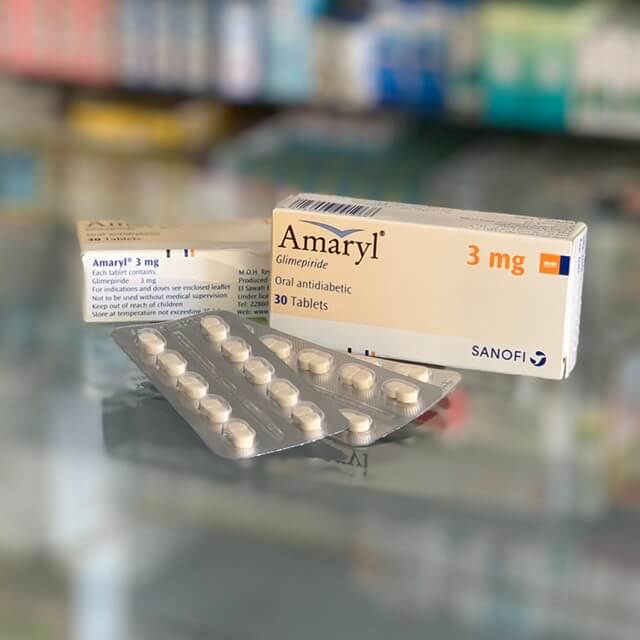
Amaryl 3 mg 30 tablets
87£
View analogsTreating type 2 diabetes when diet, exercise, and weight loss are unable to control blood sugar levels.
Buy
Product quantities
Form of Release: Tablets
Product Brand: Sanofi Egypt
Product Categories: Diabetes
Tradename:
Amaryl
Amaryl
Structure:
Each tablet contains:
Glimepiride – 3mg.
Auxiliary components:
lactose monohydrate, starch sodium gluconate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone (25,000), iron oxide yellow.
Properties:
Amaryl is an oral medication to lower blood sugar levels. This medicine belongs to a group of drugs for lowering blood sugar called sulfonylurea derivatives. The drug increases the amount of insulin released from the pancreas. Insulin then lowers blood sugar levels.
Indications:
Treating a certain form of diabetes (type 2 diabetes) when diet, exercise, and weight loss are unable to control blood sugar levels.
Mode of application:
Inside, before or with the first main meal (usually breakfast). It is important not to skip meals when you are taking Amaryl. The dose will depend on your needs, condition, and blood sugar and urine test results, and will be determined by your doctor. Do not take more tablets than your doctor tells you. The usual starting dose is 1 tablet of Amaryl, 1 mg once a day. If necessary, according to the doctor’s prescription, it is possible to increase the dose after every 1-2 weeks of treatment. The maximum recommended dose is 6 mg per day. If you forget to take a pill, you do not need to take a double dose.
Contraindications:
Type 1 diabetes mellitus; diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic precoma and coma; severe violations of liver and kidney function, incl. patients on hemodialysis (lack of clinical experience of use); pregnancy, lactation; childhood; rare hereditary diseases such as galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption; hypersensitivity to drug components or other sulfonylurea derivatives.
Precautions:
In special clinical stressful conditions, such as trauma, surgery, infections occurring with febrile temperature, metabolic control may deteriorate in patients with diabetes mellitus, therefore, temporary transfer to insulin therapy may be required to maintain adequate metabolic control. In the first weeks of treatment, the risk of hypoglycemia may increase, which requires particularly careful monitoring of the blood glucose concentration. Patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency should be especially careful when prescribing glimepiride, it is preferable to use hypoglycemic agents that are not sulfonylurea derivatives. Hypoglycemia can be quickly resolved by immediate intake of rapidly absorbing carbohydrates (glucose or sucrose). As with other sulfonylurea derivatives, despite the initial successful relief of hypoglycemia, hypoglycemia may recur. Therefore, patients must remain under constant supervision. In case of severe hypoglycemia, immediate treatment and medical supervision are additionally required, and in some cases, hospitalization of the patient. During treatment with glimepiride, regular monitoring of liver function and peripheral blood counts (especially the number of leukocytes and platelets) is required. In case of severe hypoglycemia, serious changes in the blood picture, severe allergic reactions, liver failure, the patient should immediately inform the attending physician, stop taking the drug and not resume taking it without a doctor’s recommendation.
Side effects:
Symptoms of hypoglycemia – headache, hunger, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, drowsiness, sleep disturbances, anxiety, aggressiveness, impaired concentration, confusion, speech disorders, visual disturbances, tremors, sensory disturbances, loss of self-control, cerebral cramps, drowsiness or loss of consciousness up to coma, shallow breathing, bradycardia. The clinical picture of severe hypoglycemia may resemble a stroke. Symptoms of hypoglycemia almost always disappear after its elimination. A temporary change in the swelling of the lenses, depending on the concentration of glucose in the blood, and due to this, a change in the refractive index of the lenses. Nausea, vomiting, feeling of heaviness or fullness in the epigastrium, abdominal pain, diarrhea; hepatitis, cholestasis, and jaundice, which can progress to life-threatening liver failure. Hemolytic anemia. Itching, urticaria, skin rash. If symptoms of hives develop, you should see a doctor immediately.
Storage:
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25C in the original packaging, out of reach of children.
Packaging:
The cardboard box contains 1,2 or 3 blisters of 10 tablets each, paper instructions.
Tags, Keywords:
Active Ingredients:
No comments yet. Be the first to write one.
Your comment will be published after moderation.
You’ll receive a notification to your email when someone replies.
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي