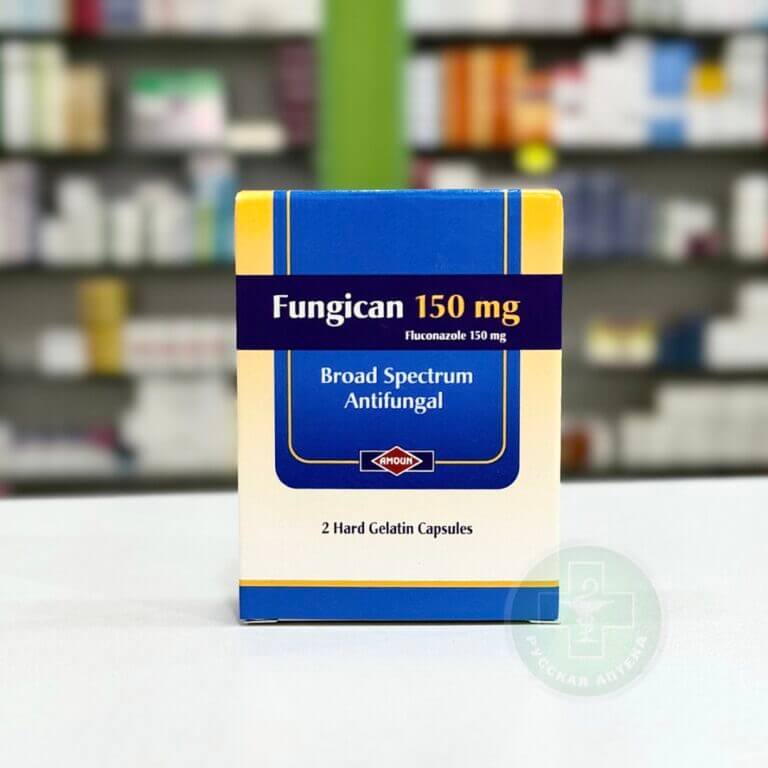
Fungican 150 mg 2 capsules
E 36
For the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis, coccidioidomycosis, invasive candidiasis. Treatment of vaginal candidiasis, acute or recurrent; candidal balanitis, when local therapy is not suitable. To prevent a decrease in the frequency of relapses of vaginal candidiasis (4 or more episodes per year).
Description of the drug
Composition:
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Fluconazole 150mg
Auxiliary components: microcrystalline cellulose, dibasic calcium phosphate, Povidone K30, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, purified talc, gelatin, titanium dioxide.
Properties:
Fluconazole is an antifungal triazole. It is a potent and selective inhibitor of fungal enzymes required for the synthesis of ergosterol. Active against opportunistic mycoses such as infections caused by Candida spp. including systemic candidiasis in animals with weakened immunity; with Cryptococcus neoformans, including intracranial infections, with Microsporum spp. and with Trichophyton spp. Fluconazole is very specific for fungal cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes. It has been shown that fluconazole does not affect plasma testosterone concentration in men or steroid concentration in women of childbea age when taken 50 mg daily for up to 28 d No clinically significant effect was observed on endogenous steroid levels or on ACTH
stimulated response in healthy male volunteers. taking fluconazole 200-400 mg per day. Interaction studies with antipyrine show that a single or multiple dose of fluconazole 50 mg does not affect metabolism.
Indications:
For the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis, coccidioidomycosis, invasive candidiasis. Treatment of vaginal candidiasis, acute or recurrent; candidal balanitis, when local therapy is not suitable. To prevent a decrease in the frequency of relapses of vaginal candidiasis (4 or more episodes per year). Prevention of candidal infections in patients with long-term neutropenia (for example, in patients with hematologic malignancies receiving chemotherapy or in patients receiving hematopoietic stem cell transplantation).
Mode of application:
The capsules should be swallowed whole and taken with or without food. The dose should be based on the nature and severity of the fungal infection. Treatment for multiple-dose infections should be continued if clinical parameters or laboratory tests indicate that active fungal infection has subsided. An
inadequate treatment period can lead to a relapse of the active infection. In adults:
Genital candidiasis: Acute vaginal candidiasis: 150 mg as a single dose. Shackled balanitis single dose. Treatment and prevention of recurrent vaginal candidiasis 150 mg in three days for a total of 3 doses (days 1, 4 and 7), followed by 150 mg once a week with a maintenance dose. Maintenance dose: 6 months.
Dermatomycosis: foot fungus, ringworm, inguinal fungus and candidal infections: 150 mg once a week for 2-4 weeks, foot fungus may require treatment for up to 6 weeks. Pityriasis versicolor: 300-400 mg once a week for 1-3 weeks. Onychomycosis: 150 mg once a week. Treatment should be continued until the infected nail is replaced (an uninfected nail grows). Toenail repair usually takes 3 to 6 months and toenails 6 to 12 months. The growth rate of different people can vary greatly with age.
Special populations: Elderly: Dosage should adjusted based on renal function (see Table Renal Failure: No Adjustment Needed With should receive 100% of the recommended dose after each dialysis; on dialysis days, patients should receive a reduced dose in accordance with hepatic impairment: there are limited data in patients with genital clearance and creatinine impairment, so fluconazole should be used with caution in patients with liver dysfunction. Children: Safety and efficacy for genital candidiasis in children has not been established. If treatment of genital candidiasis is mandatory for adolescents (12 to 17 years old), then the dosage should be the same as in adults.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to fluconazole, related azole compounds or any of the excipients in the composition. Fluconazole should not be taken with terfenadine, cisapride or ergot derivatives.
Precautions:
Use with caution in patients with renal and hepatic dysfunction. The drug has been associated with rare cases of severe liver toxicity. In cases of hepatotoxicity associated with fluconazole, there was no clear relationship with the total daily dose, durati of therapy, gender or age of the patient. It is reversible upon discontinuation of therapy. The patient should be informed of the symptoms of a serious hepatic effect (asthenia, anorexia, persistent nausea, vomiting and jaundice are important). Fluconazole treatment should be stopped immediately and the patient should see a doctor.
Cardiovascular: Several azoles, including fluconazole, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on an electrocardiogram. Simultaneous administration of fluconazole and halofantrine is not recommended.
Dermatologic reactions: Patients rarely develop skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrosis during treatment with fluconazole. Hypersensitivity: In rare cases, anaphylaxis has been reported.
Terfenadine: Coadministration of fluconazole at doses below 400 mg per day with terfenadine should be closely monitored.
Since the drug contains lactose, patients wi rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance or glucose-galactose
malabsorption should not take this medicine.
Side effects:
Most common: headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, elevated alkaline phosphatase levels, and rash. Diseases of the blood and lymphatic system: anemia. Rarely: agranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia. Immune system disorders: rare anaphylaxis. Metabolism and nutritional disorders: infrequently: decreased appetite. Rarely:
hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypokalemia. Mental disorders: drowsiness, insomnia. Nervous system disorders: infrequently: convulsions, paresthesia, dizziness, taste perversion. Rare: tremors. Gastrointestinal disorders: infrequently:
constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, dry mouth. Rare: liver failure, hepatocellular necrosis, hepatitis, hepatocellular damage. Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: general: rash. Uncommon: drug rash, urticaria, itching, increased sweating. Rare: angioedema, facial edema, alopecia. Musculoskeletal system and connective tissue: infrequently: myalgia. General disorders: fatigue, malaise, astheni fever.
Pregnancy and lactation: A study showed that women who received fluconazole in the first trimester of pregnancy had an increased risk of spontaneous abortion. There have been reports of multiple congenital anomalies in children whose mothers have been treated for at least 3 months or more with high doses (400-800 mg daily amount of fuconazole for coccidioidomycosis. The relationship between the use of fuconazole and these events is reduced to the appointment of fluconazole in standard doses and short-term treatment). Should not be used during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary after consulting a doctor.
Fluconazole passes into breast milk.
Breastfeeding can be maintained after a single dose of 200 mg or less of a standard dose of fluconazole. Not recommended after repeated use or after taking a large dose of fluconazole.
Impact on ability to drive: Patients should be warned of the possibility of dizziness or seizures while taking fluconazole, and should not be advised to drive because of these obvious side effects.
Storage:
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30C in a dry place out of the reach of children.
Packaging:
The cardboard box contains 1,2,3 blisters of 1 capsule each and paper instructions.
For the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis, coccidioidomycosis, invasive candidiasis. Treatment of vaginal candidiasis, acute or recurrent; candidal balanitis, when local therapy is not suitable. To prevent a decrease in the frequency of relapses of vaginal candidiasis (4 or more episodes per year)
For the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis, coccidioidomycosis, invasive candidiasis. Treatment of vaginal candidiasis, acute or recurrent; candidal balanitis, when local therapy is not suitable. To prevent a decrease in the frequency of relapses of vaginal candidiasis (4 or more episodes per year).
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي