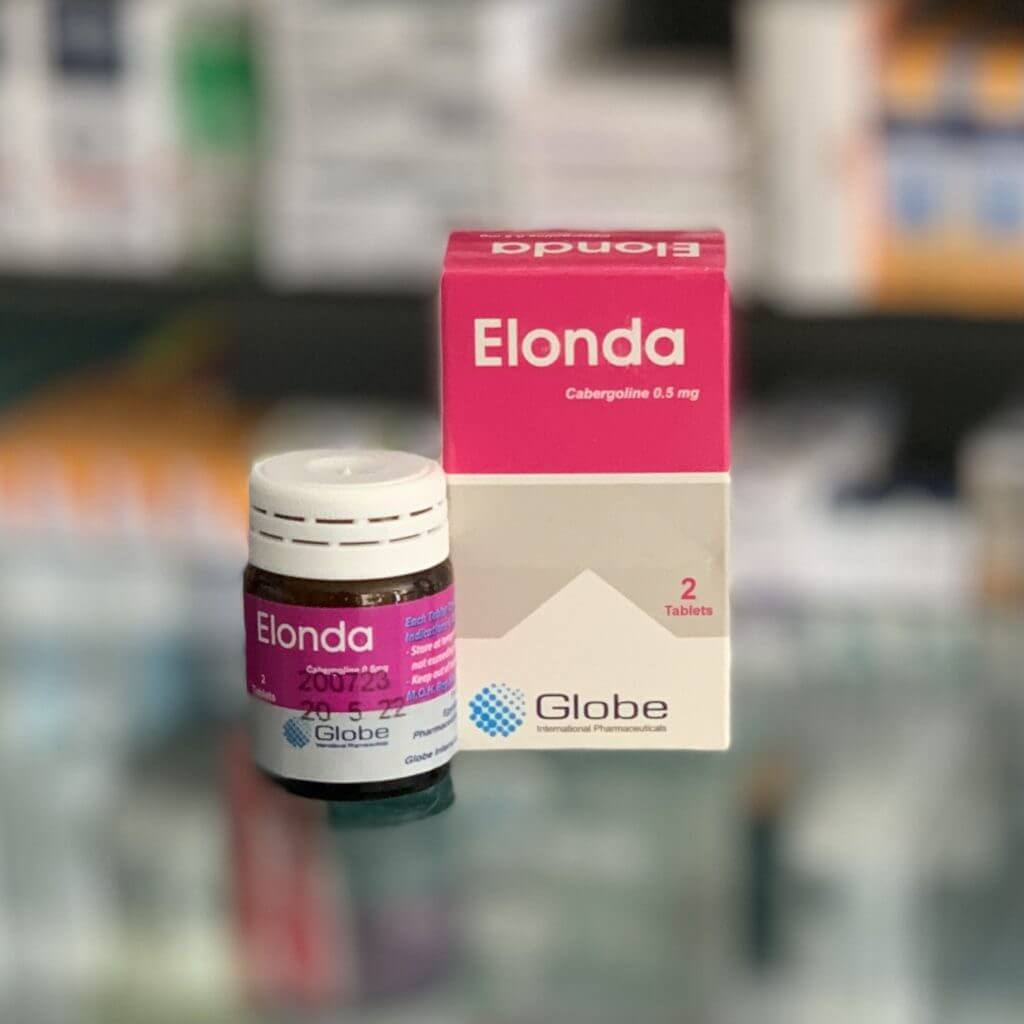
Dostinex
Composition:
Each tablet contains:
Cabergoline 0.5 mg
Auxiliary components:
lactose, leucine.
Properties:
Cabergoline is a dopaminergic derivative of ergoline, characterized by a pronounced and prolonged prolactin-lowering effect due to direct stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors of lactotropic pituitary cells. In addition, when taken at doses in excess of those to reduce plasma prolactin concentration, cabergoline has a central dopaminergic effect due to stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors.
A decrease in the concentration of prolactin in the blood plasma is observed within 3 hours after taking the drug and persists for 7-28 days in healthy volunteers and patients with hyperprolactinemia, and up to 14-21 days in women in the postpartum period.
Cabergoline has a strictly selective effect, does not affect the basal secretion of other pituitary hormones and cortisol. The prolactin-lowering effect of cabergoline is dose-dependent, both in terms of severity and duration of action.
Indications:
– prevention of physiological lactation after childbirth;
– suppression of established postpartum lactation;
– treatment of disorders associated with hyperprolactinemia, including amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, anovulation and galactorrhea;
-prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas (micro- and macroprolactinomas), idiopathic hyperprolactinemia, empty sella syndrome in combination with hyperprolactinemia.
Dosage and administration:
Taken orally, during meals.
Prevention of lactation: 1 mg (2 tablets of 0.5 mg) once on the first day after childbirth (preferably with the first meal after childbirth).
Suppression of established lactation: 0.25 mg (1/2 tab.) 2 times / day every 12 hours for 2 days (total dose is 1 mg). In order to reduce the risk of orthostatic arterial hypotension in a woman, a single dose of cabergoline should not exceed 0.25 mg.
Contraindications:
– hypersensitivity to cabergoline and / or any excipient in the preparation, as well as to any ergot alkaloids;
– fibrotic changes in the lungs, pericardium or retroperitoneal space in history;
– with long-term therapy: anatomical signs of pathology of the valvular apparatus of the heart (such as thickening of the valve leaflet, narrowing of the valve lumen, mixed pathology – narrowing and stenosis of the valve), confirmed by an echocardiographic study conducted before the start of therapy;
– lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption;
-children and adolescents under 16 years of age (safety and effectiveness of use have not been established);
-pregnancy (due to the lack of clinical data on the efficacy and safety of cabergoline);
– the period of breastfeeding (due to the lack of clinical data on the efficacy and safety of cabergoline).
Precautionary measures:
Before prescribing cabergoline therapy for the treatment of disorders associated with hyperprolactinemia, a complete study of pituitary function should be performed.
Before starting long-term cabergoline therapy, all patients should undergo a cardiovascular examination, including echocardiography (to rule out asymptomatic heart defects). In addition, it is advisable to determine CRP or other markers of inflammation, chest x-ray, study of lung function and kidney function.
Side effects:
Mental disorders: often – depression; infrequently – increased libido.
From the nervous system: very often – headache, dizziness / vertigo.
From the side of the cardiovascular system: very often – damage to the heart valves (valvulopathy), incl. regurgitation.
From the digestive system: very often – nausea, dyspepsia, gastritis, abdominal pain; often – constipation, vomiting.
From the side of the liver and biliary tract: the frequency is unknown – impaired liver function.
Storage method:
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 degrees. In a dry place.
Package:
The cardboard pack contains a glass jar of 2 tablets, paper instructions.
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي