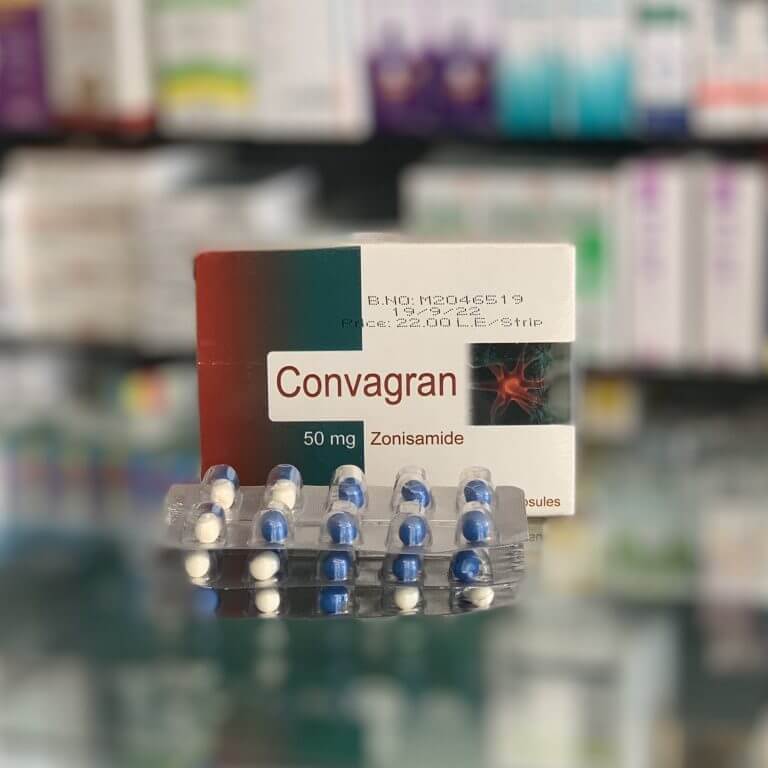
Convagran 50 mg 30 capsules
66£
View analogs-monotherapy in adult patients with partial epileptic seizures with or without secondary generalization, with newly diagnosed epilepsy; – as part of additional therapy in adults, adolescents and children from 6 years of age with partial epileptic seizures with or without secondary generalization.
Buy
Product quantities
Form of Release: Capsules
Product Brand: Mash Premiere for Pharmaceutical Industries
Product Categories: Brain and cerebral circulation • Epilepsy
Tradename:
Convagran
Convagran
Composition:
Each capsule contains:
Zonisamide 50 mg
Auxiliary components:
hydrogenated vegetable oil; MCC; sodium lauryl sulfate.
Capsule shell: gelatin; titanium dioxide (E 171); iron dye black oxide (El 72); dye red charming (E 129); dye sunset yellow (E 110), ink 1014 Tekprint SW-9008 (shellac, propylene glycol, potassium hydrochloride, iron dye black oxide
(E172)
Properties:
Zonisamide is an antiepileptic agent derived from benzisoxazole; in vitro it weakly inhibits carbonic anhydrase. Chemically, its structure differs from other antiepileptic drugs.
The mechanism of action of zonisamide is n fully understood, it probably blocks voltagesensitive sodium and calcium channels,
reduces the severity of synchronized neuronal excitation, inhibits the development of seizures and prevents further spread of epileptic activity. Zonisamide also reduces the seizure activity of neurons by increasing the inhibitory effect of GABA.
Indications:
-monotherapy in adult patients with partial epileptic seizures with or without secondary generalization, with newly diagnosed epilepsy;
– as part of additional therapy in adults, adolescents and children from 6 years of age with partial epileptic seizures with or without secondary generalization.
Method of administration and dosage:
Inside, with water, during meals or regardless of the meal. The dose of the drug is selected taking into account the therapeutic effect. As shown by clinical studies, a daily dose of 300500 mg is effective, although some patients, in particular those who do not take drugs that induce cytochrome CYP3A4, may respond lower doses.
The starting dose is 50 mg in two divided doses. After one week of administration, the daily dose can be increased to 100 mg per day. The dose can then be increased by 100 mg every 7 days, up to the maximum recommended dose of 500 mg per day. Subsequently, during treatment, you can switch to a single dose of the drug every day.
The use of two-week intervals should be considered for patients with hepatic or renal impairment, as well as for patients not taking drugs that induce cytochrome CYP3A4.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to drug components or sulfonamides. Not recommended:
-With children under 18 years of age;
-With severe liver failure;
In acute renal failure or with clinically indicated steady increase in serum creatinin
-When pregnant;
-During lactation.
Precautions:
It is recommended to cancel the drug
Konvagran@ in patients who have skin rashes that cannot be explained by other reasons. All patients with the appearance of skin rashes while taking Convagran@ should be closely monitored, especially patients who are simultaneously taking other antiepileptic drugs, which themselves can cause skin rashes.
Withdrawal syndrome.
Cancellation of the drug Konvagran@ is performed by gradually reducing the dose in order to avoid the occurrence of epileptic seizures. There is insufficient data on the cancellation of concomitantly used AEDs after seizure control is achieved with the use of Convagran@ as part of adjuvant therapy for the transition to monotherapy with
Convagran@. Therefore, the withdrawal of concomitant antiepileptic treatment should be carried out with caution.
Side effects:
Convagran@ contains a sulfonamide group. Serious adverse reactions from the immune system associated with taking drugs that contain a sulfonamide group include the appearance of a skin rash and other allergic reactions, as well as the development of severe hematological disorders, including aplastic anemia, in very rare cases leading to fatal the outcome.
The most common adverse reactions in controlled studies of combination therapy were drowsiness, dizziness, and anorexia. The most common adverse reactions in a randomized controlled trial of zonisamide monotherapy versus sustained-release carbamazepine in the zonisamide group were decreased bicarbonate levels, loss of appetite, and weight loss.
Storage method:
At a temperature not higher than 30. In a dry place.
Packaging:
The cardboard box contains 1, 2 or 3 blister 10 capsules.
Tags, Keywords:
Active Ingredients:
No comments yet. Be the first to write one.
Your comment will be published after moderation.
You’ll receive a notification to your email when someone replies.
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي