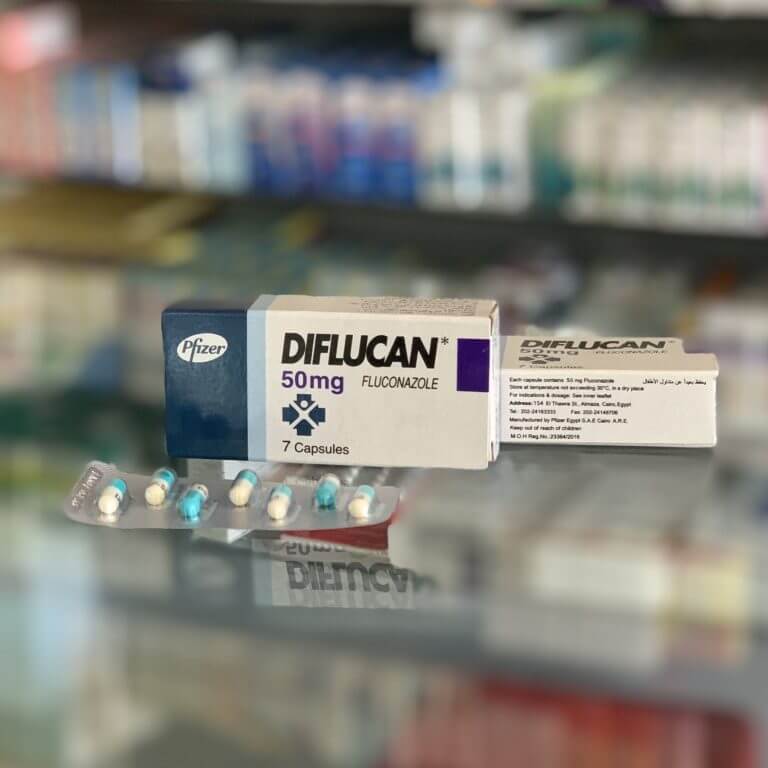
Diflucan
Composition:
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Fluconazole 50mg
Auxiliary components: lactose monohydrate, corn starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate.
Properties:
Fluconazole – has the ability to effectively inhibit the synthesis of sterols in fungal cells. The effectiveness of Diflucan has been proven against yeast and yeast-like fungi (Candida spp, Cryptococcus neoformans), molds (Histoplasma capsulatum, Blastomyces dermatitides), dermatophytes (Trichophyton spp, Microsporum immitides), dimorphic for (Coccidio.
Indications:
Candidiasis of the mucous membranes, including the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx, esophagus, non-invasive bronchopulmonary infections, candiduria, mucocutaneous and chronic atrophic oral candidiasis (associated with wearing dentures), incl. in patients with normal and
suppressed immune function. Prevention of recurrence of oropharyngeal candidiasis in AIDS patients.
Genital candidiasis; acute or recurrent vaginal candidiasis; prevention in order to reduce the frequency of relapses of vaginal candidiasis (4 or more episodes per year); candidal balanitis. Prevention of fungal infections in patients with malignant tumors, predisposed to such infections as a result of cytotoxic chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Mycoses of the skin, including mycoses of the feet, body, groin, pityriasis versicolor, onychomycosis and skin candidal infections; deep endemic mycoses in patients with normal immunity, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, sporotrichosis and histoplasmosis.
Mode of application:
Diflucan@ is taken orally. The capsules must be swallowed whole and with or without food.
The selection of the dose is carried out depending on the type and severity of the funqal infection. Treatment for those types of
infections that require multiple doses should be continued until clinical findings or laboratory tests indicate that the active fungal infection has stopped. An insufficient course of treatment can lead to a relapse of the active infection.
Adult use. Treatment of cryptococcal meningitis: the daily dose is 400 mg on the first day, the subsequent dose is 200-400 mg per day for 6 to 8 weeks. In cases of treatment of life-threatening infections, the daily dose can be increased to 800 mg. Supportive care to prevent relapse of cryptococcal meningitis in patients at high risk of relapse: 200 mg daily for the time period prescribed by the treating physician.
Coccidioidomycosis: 200-400 mg for 11-24 months or longer, depending on the patient’s condition. For some infections, especially those involving the meninges, a dose of 800 mg per day may be considered.
Invasive candidiasis: the saturating dose is 800 mg on the first day, followed by 400 mg per day. The general recommendation for the duration of treatment for candidemia is 2 weeks after the first negative result for the
presence of candidemia in the patient’s blood and the complete disappearance of symptoms of candidemia.
Treatment of mucosal candidiasis.
Oropharyngeal candidiasis: the daily dose is 200-400 mg on the first day, the subsequent dose is 100-200 mg per day for 7-21 days (until remission of oropharyngeal candidiasis is achieved). In patients with severely impaired immune function, longer periods of therapy can be used.
Esophageal candidiasis: the daily dose is 200400 mg on the first day, the subsequent dose is 100-200 mg per day for 14-30 days (until remission of esophageal candidiasis is achieved). In patients with severely impaired immune function, longer periods of therapy can be used.
Candiduria: 200-400 mg daily for 7-21 days. In patients with severely impaired immune function, longer periods of therapy can be used.
Chronic atrophic candidiasis: 50 mg daily fo 14 days.
Longer periods of therapy may be used, depending on the severity of the infection or concomitant immune dysfunction and infection.
Prevention of recurrence of mucosal candidiasis in HIV – infected patients at high risk of recurrence. Oropharyngeal candidiasis: 100-200 mg per day or 200 mg 3 times a week for the period of time prescribed by the attending physician in patients with chronically lowered immunity. Esophageal candidiasis: 100 – 200 mg per day or 200 mg 3 times a week for the period of time prescribed by the attending physician in patients with chronically lowered immunity
Genital candidiasis. Acute vaginal candidiasis:
150 mg once. Candidal balanitis: 150 mg once. Treatment and prevention of recurrence of vaginal candidiasis (4 or more episodes per year): 150 mg every three days – a total of 3 doses (on the 1st, 4th and 7th days), then a maintenance dose of 150 mg once a week within 6 months.
Dermatomycosis. Dermatophytosis of the feet, dermatophytosis of the trunk, dermatophytosis of the groin, candidiasis: 150 mg once a week or 50 mg once a day for 2 to 4 weeks, but treatment of dermatophytosis of the feet may require therapy for up to 6 weeks.
Tinea versicolor: 300 to 400 mg once a week for 1 to 3 weeks or 50 mg once a day for 2 to 4 weeks.
Dermatophytosis of the nails (onychomycosis): 150 mg once a week. Treatment should be continued until the infected nail is replaced (an uninfected nail grows). It usually takes 3 to 6 months and 6 to 12 months to repair finger and toenails. However, the growth rate can vary significantly from person to person and depending on age. In some cases, nails remain deformed after successful completion of treatment for a long-term chronic infection.
Prevention of candidal infections in patients with prolonged neutropenia: 200 – 400 mg. Treatment should begin several days before the expected onset of neutropenia and continue for 7 days after the neutrophil count has exceeded 1000 cells per mm3.
Elderly patients. In the absence of signs of renal dysfunction, the drug is prescribed in the usual dose. Renal dysfunction: no dose change is required with a single dose. Patients (including pediatric patients) with impaired renal function with repeated use of the drug should initially be given a loading dose of 50 mg to 400 mg (based on the recommended daily dose as indicated).
Patients on regular dialysis should receive 100% of the recommended dose after each dialysis; on days when there is no dialysis, patients should receive a reduced dose in accordance with their creatinine clearance.
Liver dysfunction. Data on the use of Diflucan@ in patients with impaired liver function are limited, therefore, this drug should be used with caution in such patients.
Pediatric patients. In pediatric patients, the maximum dose of 400 mg per day should not be exceeded.
As with similar infections in adults, the duration of therapy is determined by the clinical and mycological response. Diflucan prescribed as a single daily dose.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to fluconazole, related azole compounds or any of the excipients in the composition. Fluconazole should not be taken with terfenadine, cisapride or ergot derivatives. During pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Precautions:
with caution in patients with renal and hepatic dysfunction. The drug has been associated with rare cases of severe liver toxicity. In cases of hepatotoxicity associated with fluconazole, there was no clear relationship with the total daily dose, duration of therapy, gender or age of the patient. It is reversible upon discontinuation of therapy. The patient should be informed of the symptoms of a serious hepatic effect (asthenia, anorexia, persistent nausea, vomiting and jaundice are important). Fluconazole treatment should be stopped immediately and the patient should see a doctor.
Cardiovascular: Several azoles, including fluconazole, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on an electrocardiogram. Simultaneous administration of fluconazole and halofantrine
is not recommended.
Dermatologic reactions: Patients rarely develop skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrosis during treatment with fluconazole. Hypersensitivity: In rare cases, anaphylaxis has been reported.
Terfenadine: Coadministration of fluconazole at doses below 400 mg per day with terfenadine should be closely monitored.
Side effects:
From the gastrointestinal tract: decreased appetite, nausea, constipation or diarrhea, flatulence, abdominal pain, toothache, rarely liver dysfunction (icterus of the sclera, jaundice, hyperbilirubinemia, increased ALT, AST and ALP activity). From the nervous system:
headache, dizziness, excessive fatigue, rarely convulsions. From the side of hematopoietic organs: rarely – leukopenia, thrombocytopenia (bleeding, petechiae), neutropenia, agranulocytosis. Allergic reactions: skin rash, rarely – exudative erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxi epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), anaphylactoid reactions. Others: rarely – impaired renal function, alopecia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypokalemia.
Pregnancy and lactation. Data from several hundred pregnant women who received standard doses (<200 mg / day) of fluconazole, given as a single or multiple dose in the first trimester, do not show unwanted fetal defects. Despite this, the use of the drug in pregnant women is inappropriate, with the exception of severe or life-threatening forms of fungal infections, when the potential benefit of using fluconazole to the mother significantly outweighs the risk to the fetus.
Fluconazole passes into breast milk.
Breastfeeding can be maintained after a single dose of 200 mg or less of a standard dose of fluconazole. Not recommended after repeated use or after taking a large dose of fluconazole.
Impact on ability to drive: Patients should be warned of the possibility of dizziness or seizures while taking fluconazole, and should not be advised to drive because of these obvious side effects.
Storage:
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30C, out of reach of children.
Packaging:
The cardboard box contains a blister with 7 capsules and paper instructions.
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي