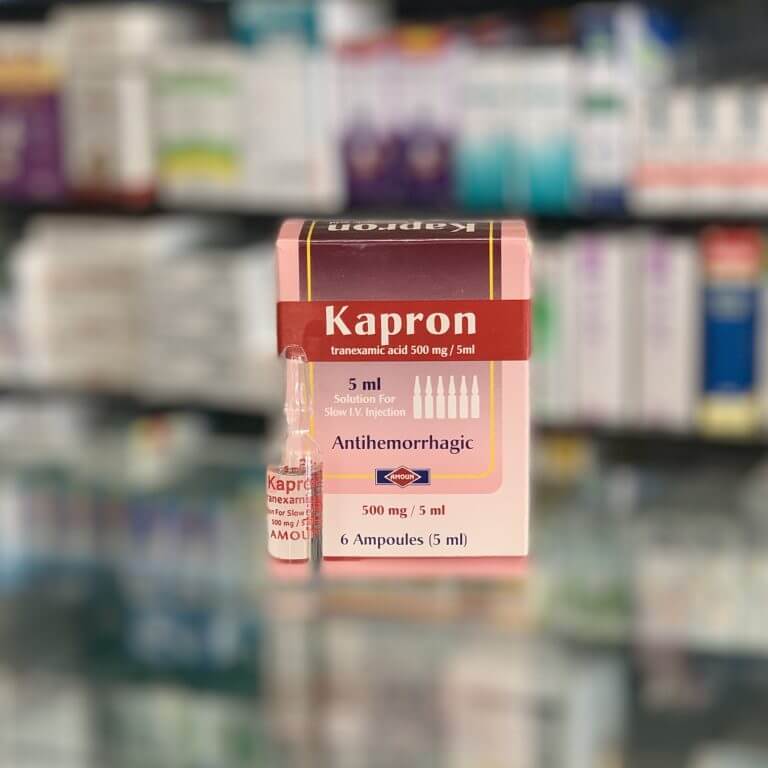
Tradename:
Kapron
Compound:
Each ampoule contains:
Tranexam 500 mg
Auxiliary components:
Water for injections
Properties:
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic agent that specifically inhibits the activation of profibrinolysin (plasminogen) and its conversion to fibrinolysin (plasmin). It has a local and systemic hemostatic effect in bleeding associated with an increase in fibrinolysis, as well as anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-infectious and anti-tumor effects by suppressing the formation of kinins and other active peptides involved in allergic and inflammatory reactions. The experiment confirmed its own analgesic activity of tranexamic acid, as well as a supertotal potentiating effect on the analgesic activity of opiates.
Indications:
– bleeding or risk of bleeding against the background of increased fibrinolysis, as generalized (bleeding during surgery and in the postoperative period, postpartum bleeding, manual separation of the placenta, chorionic detachment, bleeding during pregnancy, malignant neoplasms of the pancreas and prostate, hemophilia, hemorrhagic complications of fibrinolytic therapy, thrombocytopenic purpura, leukemia, liver disease, previous therapy with streptokinase), and local (uterine, conization of the cervix due to carcinoma, nasal, pulmonary, gastrointestinal bleeding, hematuria, bleeding after prostatectomy, tooth extraction in patients with hemorrhagic diathesis); – surgical interventions on the bladder; – surgical procedures for systemic inflammatory reactions (sepsis, peritonitis, pancreatic necrosis, severe and moderate preeclampsia, shock of various etiologies and other critical conditions).
Dosage and administration:
Intravenously (drip, jet). The recommended dose is 5-10 ml, 3 times a day.
In case of generalized fibrinolysis, a single dose of 15 mg/kg of body weight is administered every 6-8 hours, the rate of administration is 1 ml/min. With local fibrinolysis, it is recommended to administer the drug at a dose of 250-500 mg 2-3 times a day. For prostatectomy or bladder surgery, 1 g is administered during surgery, then 1 g every 8 hours for 3 days, after which they switch to oral tablet form until macrohematuria disappears.
Children:
The dose is considered at 20 mg / kg / day.
Contraindications:
-increased sensitivity to the drug;
– subarachnoid hemorrhage.
With caution: thrombohemorrhagic complications (in combination with heparin and indirect anticoagulants), thrombosis (deep vein thrombophlebitis, thromboembolic syndrome, myocardial infarction), color vision disorders, hematuria from the upper urinary tract (blood clot obstruction is possible), renal failure (cumulation is possible ).
Precautionary measures:
When combined with hemostatic drugs and hemocoagulase, activation of thrombus formation is possible. Before and during treatment, it is necessary to conduct an examination by an ophthalmologist (visual acuity, color vision, fundus).
Side effects:
Allergic reactions (rash, pruritus, urticaria), dyspepsia (anorexia, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, diarrhea), dizziness, weakness, drowsiness, tachycardia, difficult cell pain, hypotension (with rapid intravenous administration), impaired color vision, blurred vision; thrombosis or thromboembolism (the risk of development is minimal).
Package:
The cardboard box contains 6 ampoules.
 Русский
Русский English
English عربي
عربي